Spring简介
- 最基本的功能就是创建对象及管理这些对象之间的依赖关系,实现高内聚低耦合
- 方便集成第三方框架与组件
Spring启动
启动过程其实就是其IoC容器的启动过程,即建立上下文的过程
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
// 初始化Spring应用
public class SpringStart {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 加载指定的Spring配置文件
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:/META-INF/spring/applicationContext.xml");
context.start();
// 保证服务一直开着,利用输入流的阻塞来模拟
System.in.read();
}
}
Spring配置文件
配置文件通常命名为applicationContext.xml,一般会包含自动扫描包路径、jdbc、dataSource、mybatis等配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc"
xmlns:cache="http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache
http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd">
<!-- 自动扫描web包 ,将带有注解的类 纳入spring容器管理 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.eduoinfo.finances.bank.web"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 引入jdbc配置文件 -->
<bean id="propertyConfigurer" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<list>
<value>classpath*:jdbc.properties</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- dataSource 配置 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" init-method="init" destroy-method="close">
<!-- 基本属性 url、user、password -->
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
<!-- 配置初始化大小、最小、最大 -->
<property name="initialSize" value="1" />
<property name="minIdle" value="1" />
<property name="maxActive" value="20" />
<!-- 配置获取连接等待超时的时间 -->
<property name="maxWait" value="60000" />
<!-- 配置间隔多久才进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接,单位是毫秒 -->
<property name="timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis" value="60000" />
<!-- 配置一个连接在池中最小生存的时间,单位是毫秒 -->
<property name="minEvictableIdleTimeMillis" value="300000" />
<property name="validationQuery" value="SELECT 'x'" />
<property name="testWhileIdle" value="true" />
<property name="testOnBorrow" value="false" />
<property name="testOnReturn" value="false" />
<!-- 打开PSCache,并且指定每个连接上PSCache的大小 -->
<property name="poolPreparedStatements" value="false" />
<property name="maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize" value="20" />
<!-- 配置监控统计拦截的filters -->
<property name="filters" value="stat" />
</bean>
<!-- mybatis文件配置,扫描所有mapper文件 -->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean" p:dataSource-ref="dataSource" p:configLocation="classpath:mybatis-config.xml" p:mapperLocations="classpath:com/eduoinfo/finances/bank/web/dao/*.xml" />
<!-- spring与mybatis整合配置,扫描所有dao -->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer" p:basePackage="com.eduoinfo.finances.bank.web.dao" p:sqlSessionFactoryBeanName="sqlSessionFactory" />
<!-- 对dataSource 数据源进行事务管理 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" p:dataSource-ref="dataSource" />
<!-- 配置使Spring采用CGLIB代理 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true" />
<!-- 启用对事务注解的支持 -->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" />
<!-- Cache配置 -->
<cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="cacheManager" />
<bean id="ehCacheManagerFactory" class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheManagerFactoryBean" p:configLocation="classpath:ehcache.xml" />
<bean id="cacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.ehcache.EhCacheCacheManager" p:cacheManager-ref="ehCacheManagerFactory" />
</beans>
IoC & DI & AOP & Bean
- IoC Inversion of Controller
- 它就是一个创建工厂,你要什么对象,它就给你什么对象
- IoC控制反转说的是创建对象实例的控制权从代码控制剥离到IOC容器控制,实际就是你在xml文件控制,侧重于原理
- 有了IoC容器,依赖关系就变了,原先的依赖关系就没了,它们都依赖IoC容器了,通过IoC容器来建立它们之间的关系
- DI Dependency Injection
- DI依赖注入说的是创建对象实例时,为这个对象注入属性值或其它对象实例,侧重于实现
- AOP Aspect Oriented Programming
- AOP是动态代理的应用,将具体业务和相应的其它方面(比如日志,权限之类的)划分开来
- 业务不会知道还有没有其它的功能来辅助,需要的话我就给他加上一个配置就可以,而不用去修改业务代码
- Bean 一种编程规范
- 所有属性为private
- 提供默认构造方法
- 提供getter和setter
- 实现serializable接口
引入注解的原因
- 大的项目中通常会有上百个组件,如果这些组件都采用xml的bean定义来配置,显然会增加配置文件的体积,维护成本太高
- Spring2.5引入了组件自动扫描机制,它可以在类路径底下寻找标注了@Component,@Service,@Controller,@Repository注解的类,并把这些类纳入进spring容器中管理
- 注解的作用和在xml文件中使用bean节点配置组件是一样的
实现类的bean声明
- @Service 服务层组件,用于标注业务层组件,表示定义一个bean,自动根据bean的类名实例化一个首写字母为小写的bean,例如Chinese实例化为chinese,如果需要自己改名字则@Service(“your-bean-name”)
- @Controller 用于标注控制层组件(如struts中的action)
- @Repository 持久层组件,用于标注数据访问组件,即DAO组件
- @Component 泛指组件,当组件不好归类的时候,可使用这个注解进行标注
实现属性的自动装配
- @Autowired : 按类的类型进行装配
- @Resource (推荐) 不用写setter方法,该注解是属于J2EE的,减少与spring的耦合
- 如果同时指定了name和type,则从spring上下文中找到唯一匹配的bean进行装配,找不到则抛出异常
- 如果指定了name,则从上下文中查找名称(id)匹配的bean进行装配,找不到则抛出异常
- 如果指定了type,则从上下文中找到类型匹配的唯一bean进行装配,找不到或者找到多个,都会抛出异常
- 如果既没有指定name,又没有指定type,则自动按照byName方式进行装配;如果没有匹配,则回退为一个原始类型进行匹配,如果匹配则自动装配;
语法技巧
// 将sourceObj的属性拷贝给targetObj
BeanUtils.copyProperties(sourceObj, targetObj);
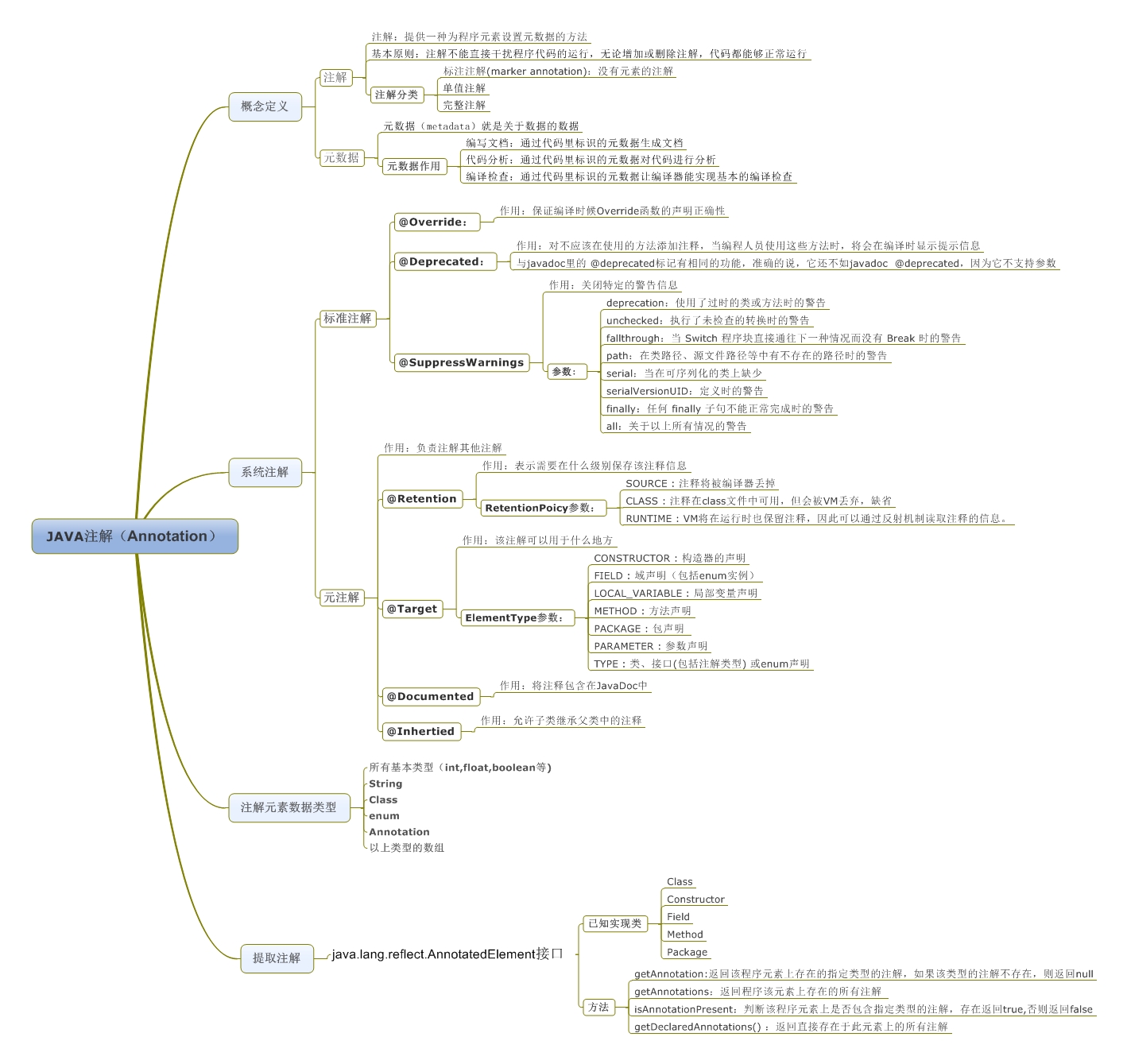
注解关系图